Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects millions of people worldwide, both children and adults. Characterized by symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, ADHD can significantly impact daily life. Recent research suggests that the limbic system, a group of structures within the brain responsible for emotion regulation, memory, and behavior, plays a crucial role in ADHD. In this blog, we will explore how the limbic system affects individuals with ADHD and discuss potential strategies to retrain parts of this system to help manage symptoms more effectively.
The Limbic System and ADHD
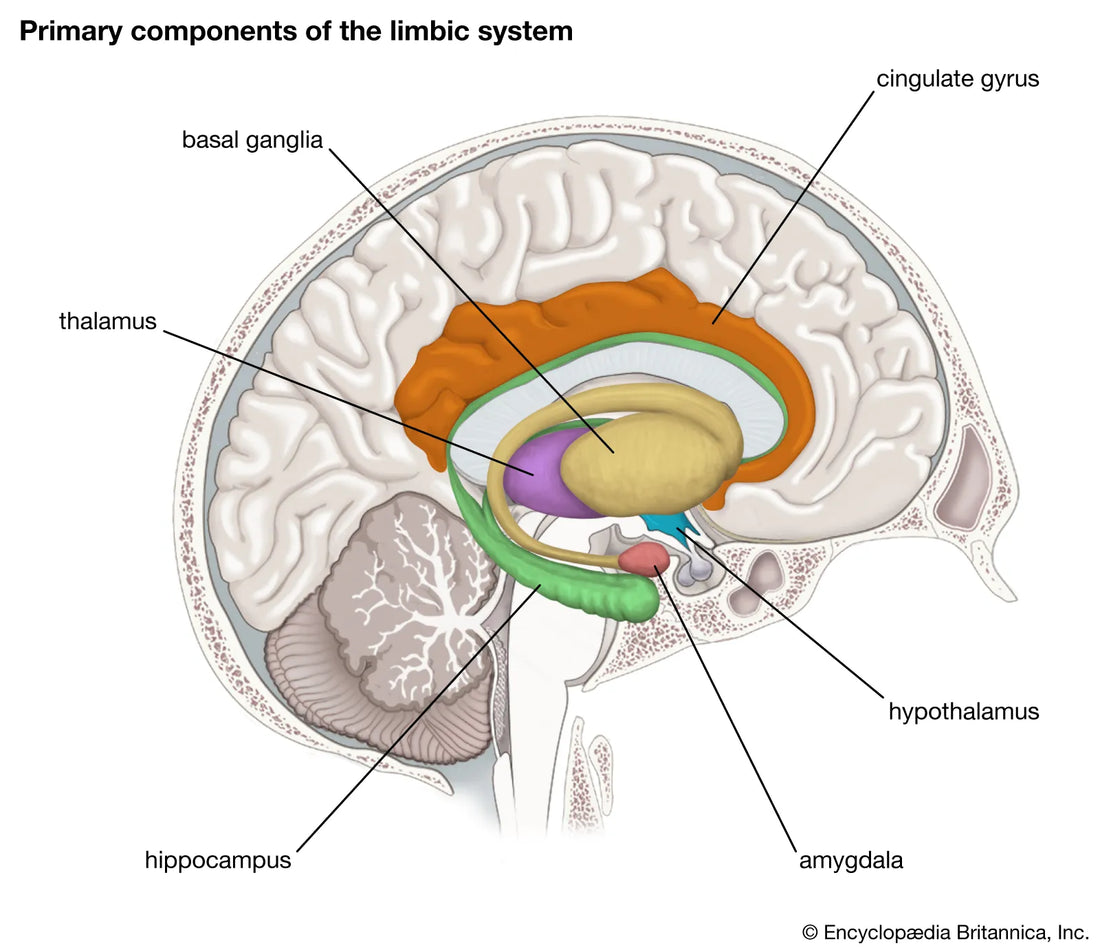
The limbic system is composed of several interconnected structures, each contributing to various aspects of emotional and cognitive function. Here's a closer look at how key components of the limbic system are involved in ADHD.
Emotional stress will cause excessive histamine release in the amygdala and limbic system. People that have a history of trauma and/or childhood abuse, are already set up for excessive histamine release. The limbic system of the brain unconsciously act to trigger the fight, flight or freeze response which has a histamine component - causing panic attacks, fast heart rate, anxiety etc. In people with a history of past trauma, the limbic system is already primed on high alert. This can lead to developing "leaky gut" and dysbiosis as well. Dysbiosis, the unhealthy imbalance of bacteria, causes even more mast cell destabilization and increased histamine release. Each area of dysregulation adds up to create a "trigger load" (Beyound Pharmaceutcials, LLC)
Amygdala
The amygdala is critical for processing emotions and is often hyperactive in individuals with ADHD. This hyperactivity can lead to heightened emotional responses, impulsivity, and difficulty in managing emotions. Emotional outbursts, anxiety, and stress are common manifestations of amygdala dysfunction in ADHD.
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is essential for forming new memories and spatial navigation. In ADHD, deficits in working memory and long-term memory are often observed, linked to hippocampal dysfunction. This can result in challenges with retaining information, following instructions, and organizing thoughts and activities.
Other Limbic Structures
- Hypothalamus: Regulates stress response and circadian rhythms, both of which can be disrupted in ADHD, leading to sleep problems and difficulty managing stress.
- Thalamus: Acts as a relay station for sensory and motor signals, with dysregulation affecting attention and focus.
Retraining the Limbic System
Given the limbic system's role in ADHD, retraining or reprogramming parts of this system, such as the amygdala and hippocampus, can be beneficial. Here are some effective strategies:
Mindfulness and Meditation
Effect on Amygdala: Regular mindfulness practice can reduce the size and activity of the amygdala, helping individuals manage their emotional responses better.
Effect on Hippocampus: Meditation can increase hippocampal volume, improving memory and cognitive function.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Effect on Amygdala: CBT helps individuals recognize and change negative thought patterns, reducing anxiety and emotional reactivity.
Effect on Hippocampus: CBT can enhance cognitive restructuring, aiding memory and organizational skills.
Exercise
Effect on Amygdala: Physical activity reduces stress and anxiety, helping to regulate the amygdala.
Effect on Hippocampus: Exercise promotes neurogenesis in the hippocampus, improving memory and cognitive function.
Neurofeedback
Effect on Limbic System: Neurofeedback can train individuals to regulate their brain activity, leading to improved attention, focus, and emotional regulation.
Diet and Limbic system
The limbic system can benefit from a diet that supports overall brain health. Here are some foods that are particularly beneficial for the limbic system:
Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel, Sardines) - Benefits: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA) that support brain structure and function. Omega-3s reduce inflammation, promote neuronal health, and support cognitive function, including memory and mood regulation.
Berries (Blueberries, Strawberries, Blackberries) - Benefits: High in antioxidants, particularly flavonoids, which help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain. Berries also support brain health by enhancing communication between brain cells.
Leafy Greens (Spinach, Kale, Swiss Chard) - Benefits: Rich in vitamins (such as folate, vitamin K, and vitamin C) and minerals (like magnesium and potassium) that support overall brain function. Leafy greens are also high in antioxidants and help reduce inflammation.
Nuts and Seeds (Walnuts, Flaxseeds, Chia Seeds) - Benefits: Good sources of healthy fats, including omega-3s and monounsaturated fats. Nuts and seeds support brain health by providing essential nutrients like vitamin E, which acts as an antioxidant.
Turmeric - Benefits: Contains curcumin, a compound with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Curcumin supports brain health by reducing inflammation, promoting neuroplasticity, and potentially enhancing mood and memory.
Dark Chocolate (High Cocoa Content) - Benefits: Contains flavonoids that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Dark chocolate also enhances mood and cognitive function by promoting the release of endorphins and serotonin.
Avocados - Benefits: Rich in healthy fats, particularly monounsaturated fats, which support brain health and improve blood flow. Avocados also contain vitamin E, vitamin C, and potassium, all of which benefit cognitive function.
Whole Grains (Oats, Quinoa, Brown Rice) - Benefits: Provide a steady source of energy for the brain through complex carbohydrates. Whole grains also contain fibre, vitamins, and minerals that support overall brain health and stabilize blood sugar levels.
Legumes (Beans, Lentils, Chickpeas) - Benefits: Good sources of complex carbohydrates, protein, and fibre. Legumes support brain health by providing sustained energy and essential nutrients like folate, iron, and magnesium.
Green Tea - Benefits: Contains caffeine and L-theanine, which promote alertness and concentration. Green tea also contains polyphenols that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, supporting brain health.
Dietary Tips for Supporting the Limbic System:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to provide essential nutrients for brain health.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Include a variety of colourful fruits and vegetables to maximize antioxidant intake, which helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources of omega-3 fatty acids (like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts) and monounsaturated fats (like avocados and olive oil) to support brain structure and function.
- Limit Sugar and Processed Foods: Minimize consumption of sugary foods and beverages, as well as processed foods high in unhealthy fats and additives, which can contribute to inflammation and impair brain function.
By incorporating these nutrient-dense foods into your diet, you can support the health and function of your limbic system, promoting better emotional regulation, memory, and overall brain health.
Supplements to Help Limbic System
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (Fish Oil) - Benefits - Omega-3s, especially EPA and DHA, are essential for brain health. They support neuronal function, reduce inflammation, and promote overall cognitive function, which can benefit the limbic system.
Magnesium - Benefits - Magnesium plays a vital role in neurotransmitter function and can help regulate stress response and mood. It supports relaxation and may benefit the amygdala and hypothalamus.
Zinc - Benefits - Zinc is involved in neurotransmitter regulation and can support cognitive function and mood stability.
Vitamin B6 - Benefits - Vitamin B6 is essential for neurotransmitter synthesis, including serotonin and dopamine, which are important for mood regulation and cognitive function.
Vitamin B12 - Benefits - B12 supports nerve health and cognitive function. It can help with memory and mood regulation, benefiting the hippocampus and overall limbic system.
Herbs for Supporting the Limbic System in ADHD
In addition to the above strategies, certain herbs can provide support to different parts of the limbic system, potentially alleviating ADHD symptoms:
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): Reduces stress and anxiety, supporting amygdala regulation.
- Bacopa (Bacopa monnieri): Enhances memory and cognitive function, supporting the hippocampus.
- Rhodiola (Rhodiola rosea): Helps manage stress and supports overall brain health.
- Ginkgo Biloba: Improves blood flow and cognitive function, supporting the hippocampus and thalamus.
- Gotu Kola (Centella asiatica): Enhances cognitive function and supports the central nervous system.
- Saffron (Crocus sativus): Helps in mood regulation and emotional stability.
- Curcumin (from Turmeric) - Curcumin has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can support brain health and protect against neurodegenerative processes in the limbic system.
Tissue Salts for the Limbic System
Tissue salts are homeopathic preparations of minerals that are believed to support cellular function and balance in the body. Here are a few that may benefit the limbic system:
Kali Phos (Potassium Phosphate) - Benefits: Known as the nerve nutrient, Kali Phos supports nervous system function and can help with stress management and emotional stability.
Mag Phos (Magnesium Phosphate) - Benefits: Supports muscular and nerve function, helping to alleviate nervous tension and promote relaxation.
Nat Mur (Sodium Chloride) - Benefits: Regulates water balance in cells and supports emotional balance, particularly in cases of grief or emotional suppression.
Conclusion
The limbic system, particularly the amygdala and hippocampus, plays a significant role in the symptoms of ADHD. By retraining these parts of the brain through mindfulness, cognitive behavioural therapy, exercise, neurofeedback, and a brain-healthy diet, individuals with ADHD can potentially improve their emotional regulation, memory, and cognitive function. Supporting these efforts with herbs known to benefit the limbic system can provide additional help. While the limbic system's involvement in ADHD is complex, targeted strategies to "retrain" it can indeed aid in managing and alleviating symptoms, leading to a better quality of life for those affected by ADHD.
Book a Personalized Consultation
If you or a loved one is struggling with ADHD, personalized treatment can make a significant difference. As a Herbal Naturopath specializing in functional medicine, I can help you find the root cause of your health issues and develop a tailored treatment plan. I use various testing methods, including genetic mutations, MTHFR polymorphisms, biochemical imbalances, and more, to get to the heart of your condition. Together, we can explore herbal remedies, lifestyle changes, and other holistic approaches to improve your health and well-being.